Aspidiophorus
- Body bottle shaped
- Furka normal
- Peduncle scales
The genus Aspidiophorus is very easily recognized microscopically by the apparent “double contour” of the body. This double contour is produced by the typical style scales of this genus, which consist of a base plate that sits directly on the cuticle. From this base plate rises a thin peduncle, which carries at its end a - usually larger - un-spined terminal plate:
 typical scales of an Aspidiophorus, here A. squamulosus.
typical scales of an Aspidiophorus, here A. squamulosus.
This results in the typical double outer contour of the animals:

- Body bottle shaped
- Furka normal
- Peduncle scales
23 Species:
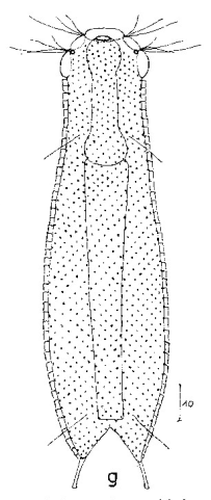
Aspidiophorus oculifer
115 µm - 135 µmDorsal scales: 17-22 rows, each with 36-41 small peduncle scales; end plates 2.5-4 µm; peduncles 0.6-1 µm; no spines
Ventral scales: 2 keeled and spined terminal plates (6.5-10.5µm); 5-12 rows of 1.5-3µm long keels
Particularities: 2 pseudocells, one-piece X-organ
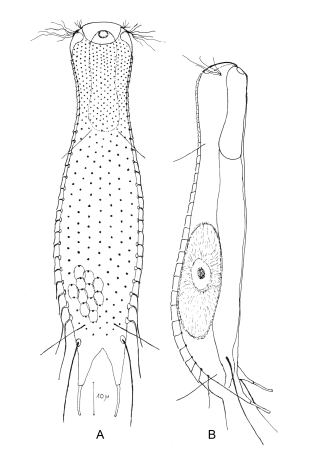
Aspidiophorus ontarionensis
120 µm - 140 µmDorsal scales: 9 rows of 16-17 peduncle scales each; end plates (6-7 x 2-3 µm) rounded anteriorly, incised posteriorly, no keels; last 2-3 rows terminate in 20 µm spines; lateral on toes a pair of spines (25 µm).
Ventral scales: Ventral intercilliary field with 25 rows of tiny petiole scales
Particularities: long spines
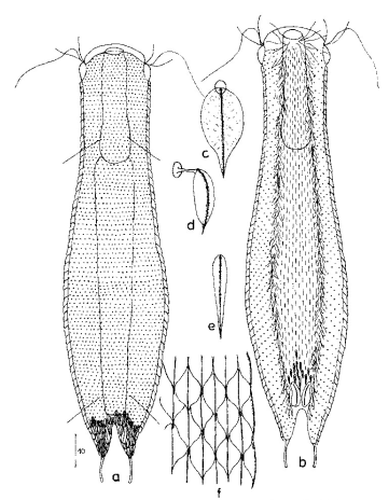
Aspidiophorus ophiodermus
92 µm - 170 µmDorsal scales: 41-44 rows of 48-50 small peduncle scales each; end plates elliptical, acuminate with keel, overlapping, 3 x 1.5 µm; two 5x2 µm peduncle scales on furca inner side.
Ventral scales: Ventral innercilliary field with two terminal plates (7x4 µm) and 10 rows of narrow, distally pointed keel scales (4x0.75µm)
Particularities: brown stomach ring
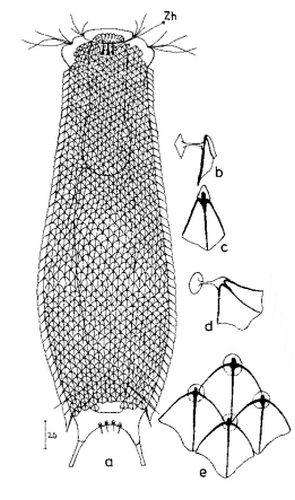
Aspidiophorus paradoxus
245 µm - 326 µmDorsal scales: 25 rows of 40-45 rhombic petiolar scales each with lateral and median keels (4x6 µm); petioles 6-7 µm; terminal plates of last terminal rows often enlarged (12-17 µm); posterior end free; between toes 4 short spines on oval scales.
Ventral scales: Ventral innerciliary field covered with petiole scales
Particularities: 3 teeth, eggs smooth (125x74 µm)
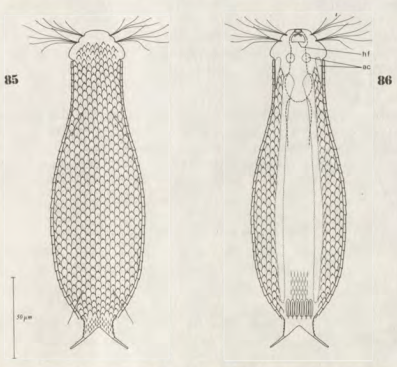
Aspidiophorus pleustonicus
191 µm - 208 µmDorsal scales: 45-53 rows of 29-32 petiole scales each (5-7 µm); no keel, not rhombic, similar shape to that of P. rhomboides
; Toe base dorsal with keels
Ventral scales:
6 keeled terminal plates; at the posterior end 10-12 rows of keels (4-4.5 µm), otherwise naked
Particularities: very small pharynx; body very broad
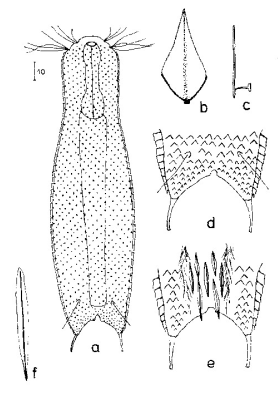
Aspidiophorus polonicus
158 µm - 172 µmDorsal scales: 18-20 rows of 42-45 small petiolar scales each; petioles 1.5 µm; terminal plates 2-3.5 µm long, proximally strengthened margin, distally acuminate, weak median keel; no spines
Ventral scales: Ventral intercilliary field naked, except for a few elongate peduncle scales; two narrow terminal plates(6.5-11.5 µm)
Particularities: without pseudocells; naked ventral intercilliary field .
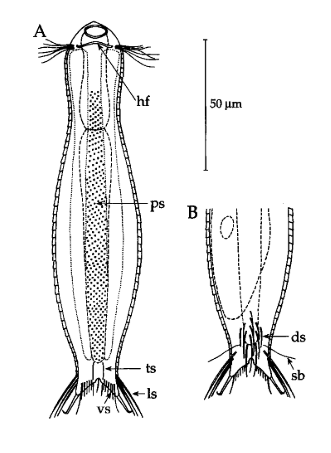
Aspidiophorus pori
141 µm - 147 µmDorsal scales: 53 petiole scales (3 µm) per row; 3 pairs of spines at outer base of toes (20-22 µm).
Ventral scales: Ventral intercilliary field very many petiole scales; a pair of terminal spines (8-10 µm) and many shorter spines protruding into the toe cutout.
Particularities: Claws on the adhesive tubes
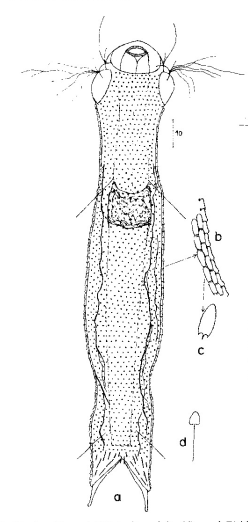
Aspidiophorus schlitzensis
120 µm - 185 µmDorsal scales: 25-30 rows, each with 60-80 minute petiolar scales; terminal plates unkeeled (0.5-2 µm), elongate, pointed distally; posterior end with elongate keel scales
Ventral scales: Ventral intercilliary field numerous longitudinal rows of minute petiolar scales; two keeled terminal plates (6-7 µm).
Particularities: Stomach ring, cephalion large
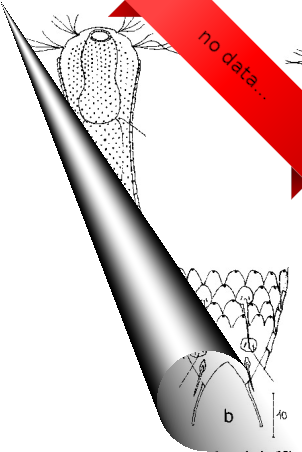
Aspidiophorus semirotundus
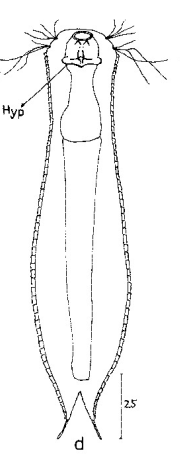
Aspidiophorus slovinensis
140 µm - 160 µmDorsal scales: 15-17 rows, each with 40-45 small petiole scales; terminal plates 2-3 µm;, rounded; no spines.
Ventral scales: Ventral intercilliary field with peduncle scales; large trapezoidal hypostomium with transverse furrow (14µm long).
Particularities: Mouth armament from 3-4 pairs of clasps and buttons