Subsections of Setopus
Setopus abarbita
Width:
Width of the head ( fünflappig ):
µm
Length of the furca:
Adhessive tubes:
Pharyx ( zylindrisch ):
Diameter of the mouth ( rund ):
unknown
Setopus aequatorialis

Width:
Width of the head ( fünflappig ):
µm
Length of the furca:
Adhessive tubes:
Pharyx ( zylindrisch ):
Diameter of the mouth ( rund ):
unknown
Setopus bisetosus
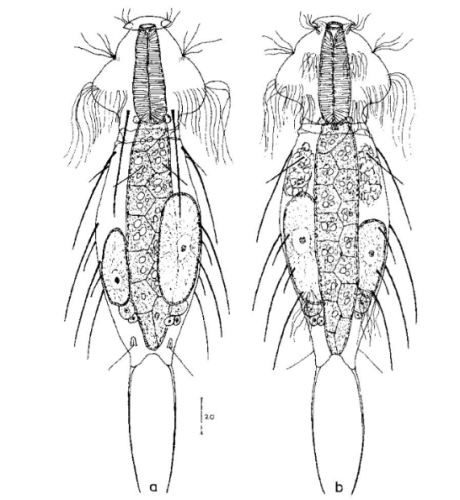
140 µm - 150 µm
Width:
40 µm - 50 µm
Width of the head ( five lobes, broad ):
38 µm - 40 µm
µm
Length of the furca:
Adhessive tubes:
Pharyx ( cylindrical ):
35 µm
Diameter of the mouth ( around ):
unknown
Dorsal scales:
posterior setolae on small keel scales; terminal spine 45µm; spines in 5 groups of one short ventral spine (10-15 µm) and one longer lateral spine (ca. 40 µm); anterior and last group unpaired, i.e. 8 spines per side
Ventral scales:
naked; only one pair of eyelashes; eyelash tufts on head typical
Oecology:
plant-rich pools; over mud; rare
Setopus bisetosus (Thomson, 1891) - a formerly common species - has become very rare due to the progress of industrial agriculture and the accompanying drainage. Therefore, it always pleases me to find a specimen of this species.
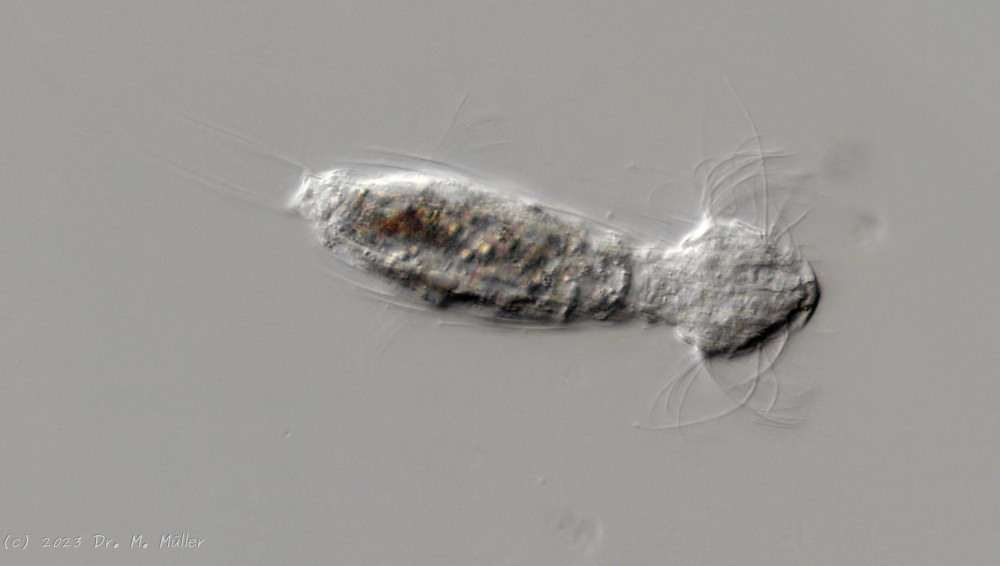
free swimming copy
Unfortunately, I could not completely still the animal, so the photo quality was not optimal.
The semi-planktic Setopus species usually do not have continuous ciliary bands and move swimming with an (almost completely closed) ciliary ring on the head. In addition, some ciliary tufts are present ventrally on the head. On the body itself, except for a few isolated cilia, the ciliary bands are reduced to a pair of ciliary tufts on the abdomen.
Ventrally the animal bears three pairs of spines.
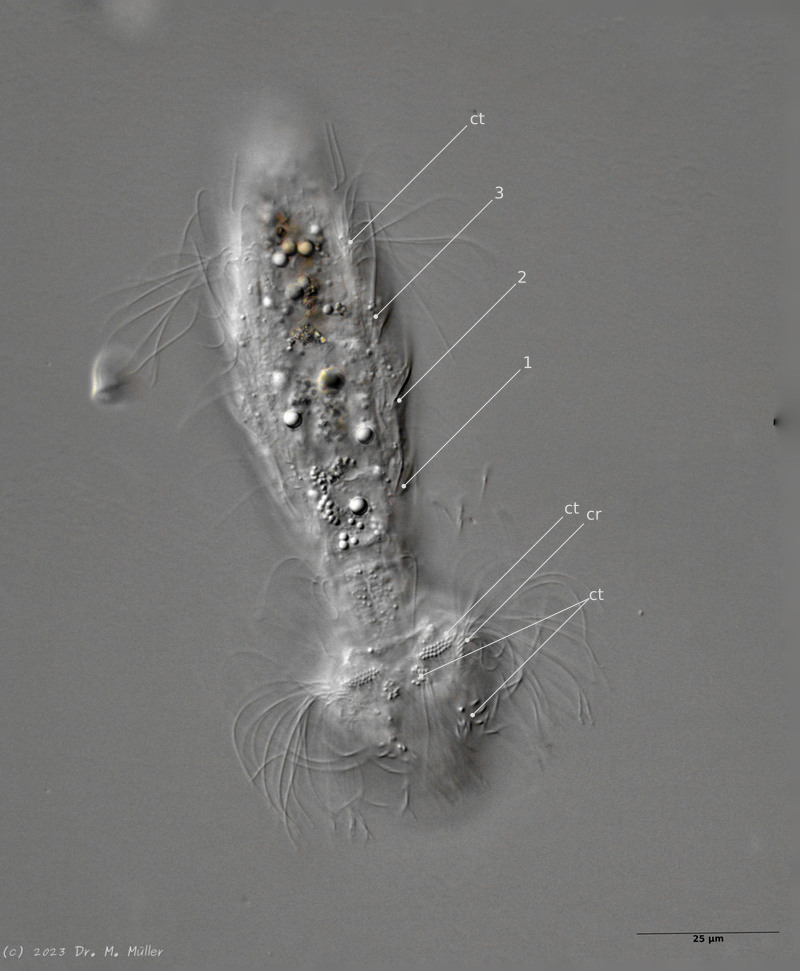
Ventral ciliations: cilia ring (cr), ciliate tuft (ct); 1..3: ventral spines.
In median section, two pairs of keeled terminal plates can be seen at the posterior end of the animal. These terminal plates are not mentioned in the literature.
Laterally five pairs of spines are visible.
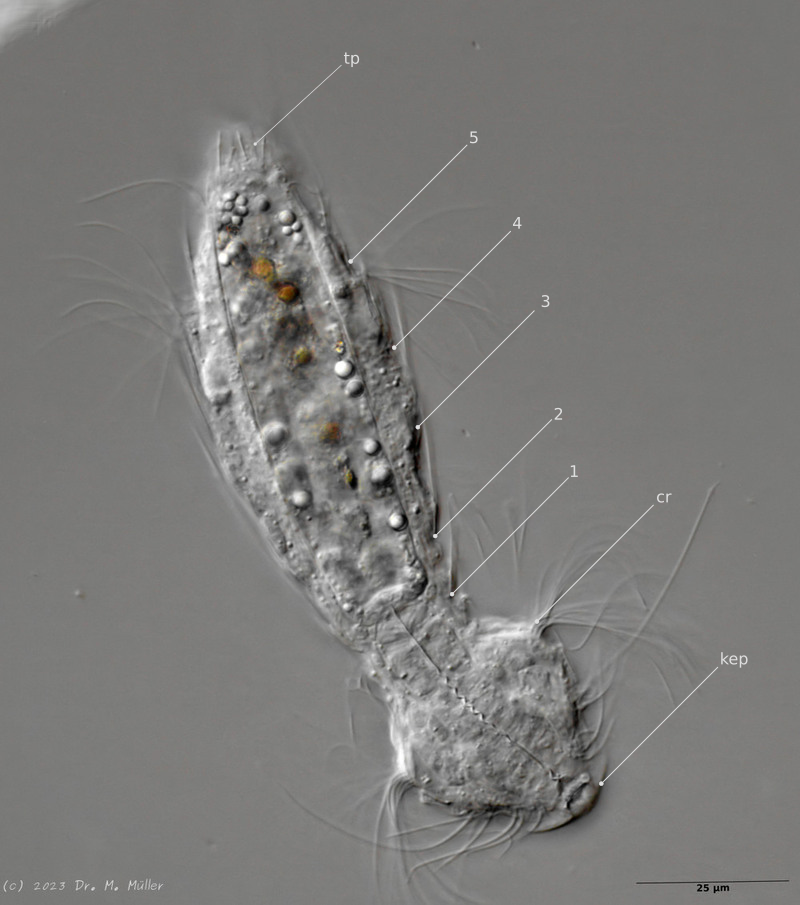
Median section with terminal plates (tp) and head shield (kep); 1..5: lateral spines; cilia ring (cr).
Typical is the broad and strong head shield (kephalion) of the animals.
Literature:
(Thompson, 1891)Setopus chatticus

Width:
Width of the head ( fünflappig ):
µm
Length of the furca:
Adhessive tubes:
Pharyx ( zylindrisch ):
Diameter of the mouth ( rund ):
unknown
Setopus dubius

Width:
Width of the head ( fünflappig ):
µm
Length of the furca:
Adhessive tubes:
Pharyx ( zylindrisch ):
Diameter of the mouth ( rund ):
unknown
Setopus iunctus

Width:
Width of the head ( fünflappig ):
µm
Length of the furca:
Adhessive tubes:
Pharyx ( zylindrisch ):
Diameter of the mouth ( rund ):
unknown
Setopus lemnicola

Width:
Width of the head ( fünflappig ):
µm
Length of the furca:
Adhessive tubes:
Pharyx ( zylindrisch ):
Diameter of the mouth ( rund ):
unknown
Setopus primus

120 µm - 186 µm
Width:
34 µm - 42 µm
Width of the head ( five-lobed ):
39 µm - 52 µm
Width of the neck:
24 µm - 26 µm
Length of the furca:
Adhessive tubes (none):
Pharyx ( cylindrical ):
40 µm - 47 µm
Diameter of the mouth ( around ):
unknown
Dorsal scales:
No scales; dorsolaterally 3 pairs of single, slightly curved spines (46µm); two simple terminal spines (40-54 µm).
Ventral scales:
no scales; 4 eyelash tufts in two rows
Oecology:
weedy bog ponds; rare
Literature:
(Grünspan, 1908)Setopus tongiorgii

84 µm - 140 µm
Width:
26 µm - 40 µm
Width of the head ( five-lobed ):
25 µm - 38 µm
µm
Length of the furca:
Adhessive tubes (none):
Pharyx ( cylindrical ):
25 µm - 29 µm
Diameter of the mouth ( around ):
unknown
Dorsal scales:
Terminal spines with secondary apices on triangular scale rudiments; unequal in length (27-30 µm; 43-55 µm); numerous dorsolateral spines with secondary apices on scale rudiments; 21 per side.
Oecology:
rare; bog lake
Similar species:
S. chatticus : no scales and fewer shorter spines
Particularities:
scaled ventral interciliate field
Setopus tongiorgii has been found so far only in Italy and some locations in Germany and is - like all Setopus species - relatively rare.
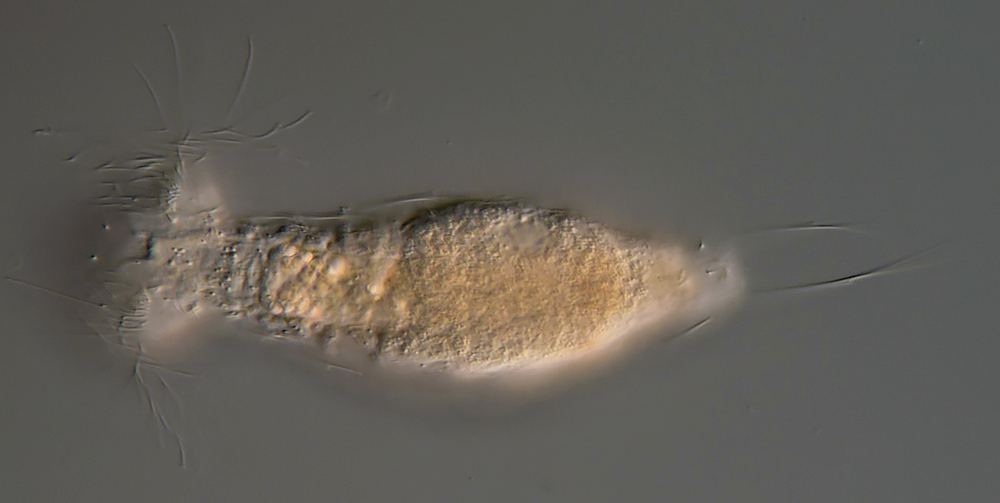
Overview with focus on the ring of eyelashes on the head ( Dr. Stephan Krall).
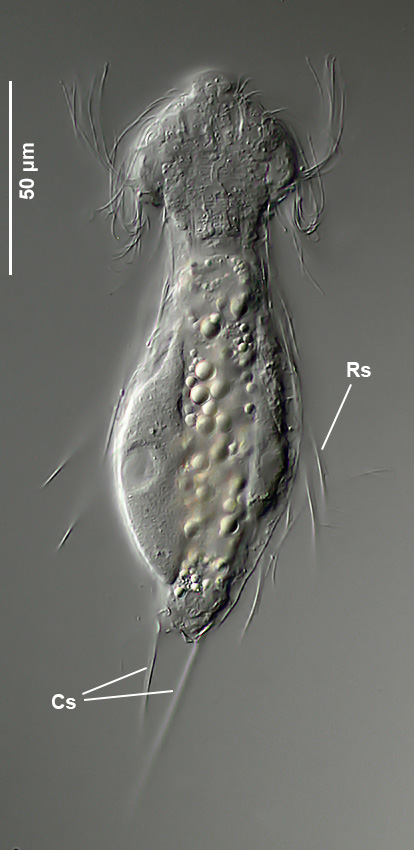
Transverse section; Rs: trunk spines; Cs: caudal spines ( Dr. Ole Riemann).
In the cross section the lateral spines with their secondary spike are well visible. Terminal are two caudal spines of unequal length, which also carry a secondary tip.
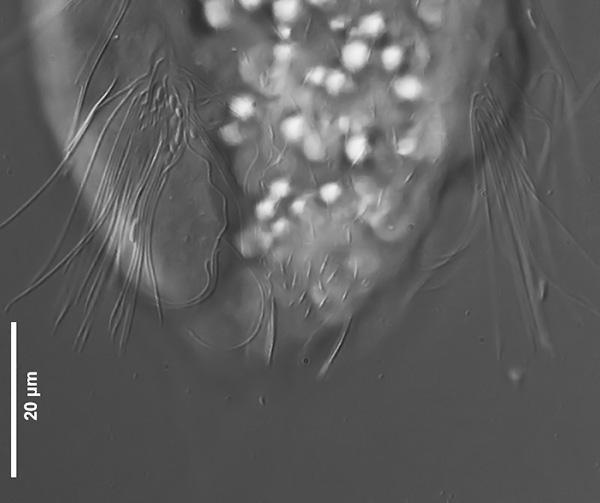

Scaling of the ventral intermediate field ( Dr. Ole Riemann).
Ventrally, the small, roundish scales and the keeled terminal plates of the ventral interciliar field can be seen. So far only in S. tongiorgii scales were found in this area. This feature is therefore of special importance for the diagnosis of the species.
Literature:
(Balsamo, 1982)
(Kieneke und Riemann 2008)
(Kieneke, Martínez Arbizu, und Riemann 2008)